
Preparing for a MySQL interview? This guide covers latest MySQL database interview questions and answers to help you succeed.
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
The basic SQL commands are:
SELECT: Retrieves data from the database.
INSERT: Adds new data to the database.
UPDATE: Modifies existing data in the database.
DELETE: Removes data from the database.
The SELECT statement is used to fetch data from a database. It can retrieve specific columns from a table using the syntax:
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name;.
The WHERE clause is used to filter records based on specific conditions. It is used in conjunction with SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc.
JOINS are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column. Types of joins include INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, and FULL JOIN.
INNER JOIN returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables.
SELECT employees.name, departments.dept_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments ON employees.dept_id = departments.id;
A subquery is a query within another query. It is used to perform operations that need to be executed in multiple steps.
SELECT name
FROM employees
WHERE dept_id = (SELECT id FROM departments WHERE dept_name = 'Sales')
An index is a database object that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a table at the cost of additional storage space.
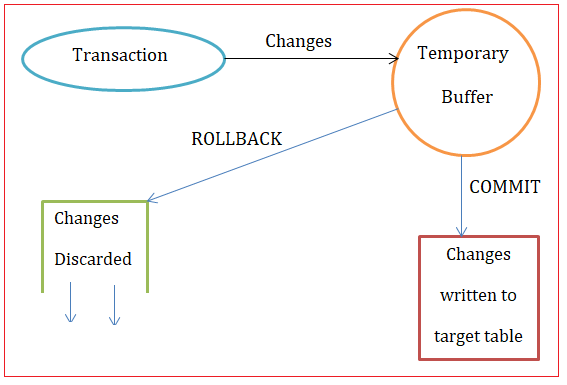
A transaction is a sequence of one or more SQL operations treated as a single unit of work, ensuring that either all operations are executed successfully or none are.
You can start a transaction using the START TRANSACTION or BEGIN command.
COMMIT: Saves the changes made during the transaction.
ROLLBACK: Undoes the changes made during the transaction.
MySQL supports several types of indexes: PRIMARY, UNIQUE, FULLTEXT, and SPATIAL.
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column1, column2);
A stored procedure is a set of SQL statements that can be stored in the database and executed repeatedly.
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name (parameters)
BEGIN
-- SQL statements
END;
Stored Procedure: Does not necessarily return a value and can perform multiple actions.
Function: Must return a single value and is typically used for computations.
Difference between Stored Procedure and Function in MySQL
| Feature | Stored Procedure | Function |
| Return Value | Does not necessarily return a value. | Must return a single value. |
| Purpose | Can perform multiple actions, such as updates and inserts. | Typically used for computations and returning results. |
| Usage in Queries | Cannot be called directly in SQL queries. | Can be called directly within SQL queries. |
| Parameters | Can have input, output, and input-output parameters. | Only accepts input parameters. |
| Transaction Management | Can handle transactions. | Cannot handle transactions. |
CREATE FUNCTION calculate_salary (base_salary DECIMAL(10,2), bonus DECIMAL(10,2))
RETURNS DECIMAL(10,2)
BEGIN
RETURN base_salary + bonus;
END;
MySQL supports various data types including:
Numeric: INT, DECIMAL, FLOAT, DOUBLE, etc.
String: VARCHAR, CHAR, TEXT, etc.
Date and Time: DATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, etc.
Binary: BLOB, BINARY, VARBINARY, etc.
Constraints are rules enforced on data columns to ensure the integrity and validity of the data. Common constraints include NOT NULL, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, and CHECK.
Constraints are rules enforced on data columns to ensure the integrity and validity of the data. Common constraints include NOT The NOT NULL constraint ensures that a column cannot have a NULL value.
The DEFAULT constraint provides a default value for a column when no value is specified during insertion.
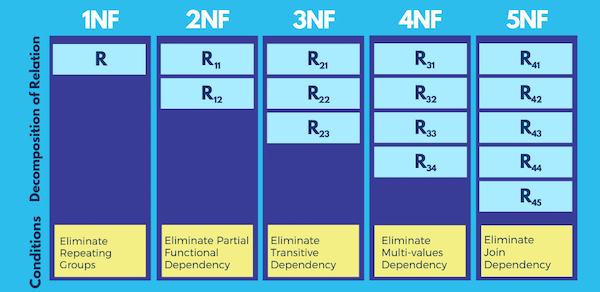
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. It involves dividing large tables into smaller tables and defining relationships among them.
The common normal forms include:
First Normal Form (1NF): Ensures that the table has no repeating groups.
Second Normal Form (2NF): Ensures that the table is in 1NF and all non-key attributes are fully functional dependent on the primary key.
Third Normal Form (3NF): Ensures that the table is in 2NF and all its attributes are not transitively dependent on the primary key.
A view is a virtual table created based on the result-set of a SELECT statement. It can simplify complex queries and enhance security by restricting access to specific data.
You create a responsive design by using media queries, flexible grid layouts, and relative units like percentages or em/rem.
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
A trigger is a database object that automatically executes a specified set of actions when certain events occur, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE on a table.
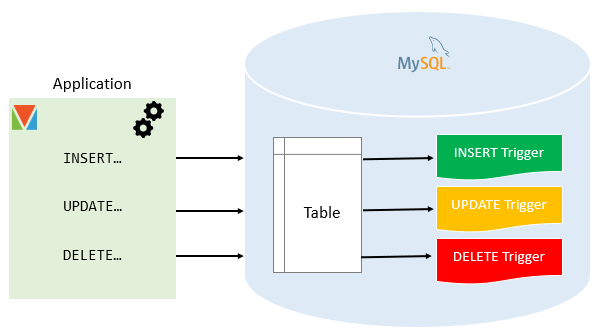
A trigger is a database object that automatically executes a specified set of actions when certain events occur, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE on a table.
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name
BEFORE INSERT ON table_name
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- Trigger logic
END;
The EXPLAIN statement provides information about how MySQL executes a query, helping in optimizing and troubleshooting queries.
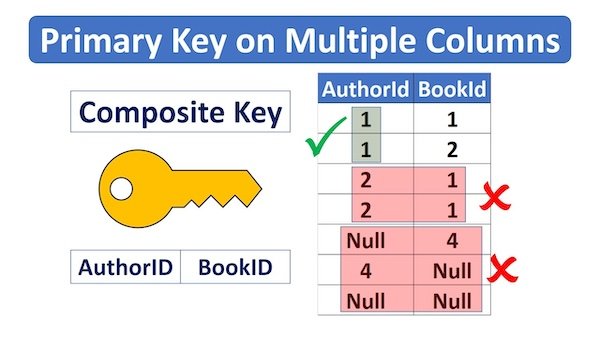
A composite key is a primary key that consists of two or more columns to uniquely identify a row in a table.
Difference between UNION and UNION ALL
| Feature | UNION | UNION ALL |
| Functionality | Combines the result sets of two or more SELECT statements and removes duplicate rows. | Combines the result sets of two or more SELECT statements and includes all duplicate rows. |
| Duplicates | Removes duplicate rows from the result set. | Includes duplicate rows in the result set. |
| Performance | Generally slower due to the additional step of removing duplicates. | Generally faster as it does not remove duplicates. |
| Use Case | Use when you need to ensure no duplicate rows in the result set. | Use when duplicates are acceptable or desired for analysis. |
The GROUP BY clause groups rows that have the same values in specified columns into summary rows, often used with aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, etc.
The HAVING clause is used to filter records. It is similar to where clause. Having clause can be used with aggregate functions whereas where clause can not be used with aggregate function.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition
GROUP BY column_name(s)
HAVING condition
ORDER BY column_name(s);
Mastering the questions and concepts outlined in this guide is essential for excelling in MySQL interviews. By thoroughly preparing with these common interview questions and their answers, you’ll be well-equipped to showcase your expertise and confidence during the interview process.
If you’re looking to further enhance your MySQL or DBMS skills and gain hands-on experience, consider joining Netmax Technologies. As a premier institution in IT training, we offer comprehensive courses ranging from 45 days to 4-6 months industrial training , designed to prepare you for real-world challenges and career success. Our experienced instructors and practical training approach ensure that you gain the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in the competitive field of Python development. Enroll today and take the first step towards becoming a proficient Python developer with Netmax Technologies!