
Python Interview Questions and Answers
Introduction
Preparing for a Python interview can be daunting, whether you’re a fresher or experienced professional. However, this guide covers latest Python interview questions and answers to help you succeed.
Basic Python Question
Python is a versatile and widely-used programming language that emphasizes simplicity and readability.
To begin with, basic Python interview questions assess a candidate’s understanding of fundamental concepts and core principles. These questions cover topics such as data types, operators, control flow, and basic syntax. Therefore, mastering these basics is crucial for anyone looking to advance in Python programming and is often the first step in any technical interview process.
1) What is Python?
It is a high-level, interpreted, and general-purpose programming language known for its readability and support. Moreover, it supports multiple programming paradigms.
2) What are the key features of Python?
Python provides key features such as simplicity, readability, extensive libraries, dynamic typing, interpreted nature, and support for multiple programming paradigms.
3) How do you declare a variable in Python?
You declare variables in Python by assigning a value to a name using the ‘=’ operator, for example, x = 10
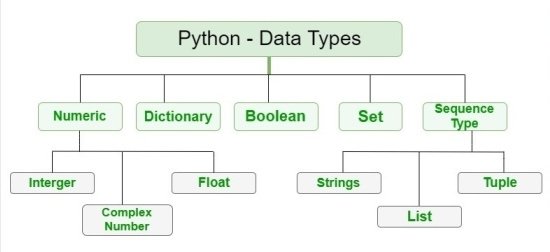
4) What are Python's built-in data types?
Common built-in data types include integers (int), floating-point numbers (float), strings (str), lists (list), tuples (tuple), dictionaries (dict), and sets (set).
5) How do you write comments in Python?
Comments in Python are written with the # symbol for single-line comments and triple quotes ”’ or “”” for multi-line comments.
#This is single line comment
'''This is
multi line
comment '''
6) How do you create a function in Python?
Functions are created using the def keyword, e.g.:
def my_function():
print("Hello, World!")
7) How do you import modules in Python?
Modules are imported using the import statement, e.g.:
import math
print(math.sqrt(16))
Data Structures in Python
Data structures are essential for organizing and managing data efficiently in Python. Interview questions in this category focus on core structures like lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. Candidates are tested on operations such as insertion, deletion, traversal, and searching, as well as the performance and application of these structures.
8) What are lists in Python?
Lists are ordered, mutable collections of items, defined using square brackets, e.g., my_list = [1, 2, 3].
9) What are tuples in Python?
Tuples are ordered, immutable collections of items, defined using parentheses, e.g., my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
10) What is a dictionary in Python?
A dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs, defined using curly braces, e.g., my_dict = {“key1”: “value1”, “key2”: “value2”}.
11) How do you sort a list of dictionaries by a key in Python?
A list of dictionaries can be sorted using the sorted() function with a lambda function as the key.
my_list = [{"name": "Alice", "age": 25}, {"name": "Bob", "age": 20}]
sorted_list = sorted(my_list, key=lambda x: x["age"])
print(sorted_list)
12) What is the difference between append() and extend() in Python?
append() adds a single element to the end of a list, while extend() adds all elements of an iterable to the end of a list.

13) How do you remove duplicates from a list in Python?
Tuples are ordered, immutable collections of items, defined using parentheses, e.g., my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
my_list = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]
my_list = list(set(my_list))
print(my_list) # Output : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
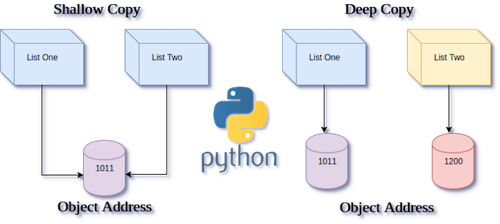
14) What is the difference between deep copy and shallow copy?
A shallow copy creates a new object but inserts references to the original objects, while a deep copy creates a new object and recursively copies all objects found in the original.
my_list = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5]
# shallow copy :
my_list1 = my_list
# deep copy:
my_list2 = my_list.copy()
Questions on Control Flow in Python
Control flow in Python determines the order in which code is executed, encompassing conditional statements, loops, and exception handling. Interview questions in this category assess a candidate’s ability to use if-else statements, for and while loops, and try-except blocks to manage the logical flow of their programs.
15) What is the difference between '==' and 'is' in Python?
‘==’ checks for value equality, while ‘is’ checks for object identity (whether two variables point to the same object in memory).
16) How do you handle exceptions in Python?
Exceptions are handled using try, except, and optionally finally blocks, e.g.:
try:
x = 1 / 0
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Cannot divide by zero")
finally:
print("Execution finished")
17) How do you handle multiple exceptions in Python?
Multiple exceptions can be handled using a tuple, e.g.:
try:
x = int("abc")
except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
print(e)
18) What is the use of the with statement in Python?
With statement simplifies exception handling by encapsulating common preparation and cleanup tasks.
# 1) without using with statement
file = open('file_path', 'w')
file.write('hello world !')
file.close()
# 2) without using with statement
file = open('file_path', 'w')
try:
file.write('hello world')
finally:
file.close()
19) What is the purpose of the pass statement in Python?
The pass statement is a null operation used as a placeholder for future code.
20) How do you check if a key exists in a dictionary?
To check if a key exists or not in keyword is used, e.g.:
my_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
if "a" in my_dict:
print("Key exists")
21) How do you perform file I/O in Python?
File I/O is performed using the open() function, e.g.:
with open("file.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read()
for index, value in enumerate(['a', 'b', 'c']):
print(index, value)
Looping in python question
Looping questions in Python interviews test your ability to use for-loops and while-loops to iterate over data structures. These questions assess your understanding of loop control, optimization, and nested loops, which are essential for efficient data processing and repetitive tasks.
22) How do you use the enumerate function in Python?
enumerate() adds a counter to an iterable and returns it as an enumerate object.
x = ('apple', 'banana', 'cherry')
y = enumerate(x)
#output: [(0, 'apple'), (1, 'banana'), (2, 'cherry')]
23) What is a list comprehension in Python?
A list comprehension is a concise way to create lists.
Syntax :
newlist = [expression for item in iterable if condition == True]
Example :
squares = [x**2 for x in range(10)]
24) What is the zip function in Python?
The zip function combines multiple iterables into a single iterator of tuples, e.g.:
list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list2 = ['a', 'b', 'c']
zipped = zip(list1, list2)
print(list(zipped))
25) How do you use the itertools module in Python?
An itertools module provides functions to create iterators for efficient looping, e.g.:
import itertools
counter = itertools.count(start=10, step=2)
print(next(counter)) # 10
print(next(counter)) # 12
26) What are the map, filter, and reduce functions in Python?
- map applies a function to all items in an input list.
- filter creates a list of elements for which a function returns true.
- reduce applies a function cumulatively to the items of a list, reducing the list to a single value.

27) How do you create a generator expression in Python?
Generator expressions are similar to list comprehensions but use parentheses instead of square brackets, e.g.:
gen_exp = (x**2 for x in range(10))
for num in gen_exp:
print(num)
28) What is a generator in Python?
A generator is a function that returns an iterator using the yield keyword, allowing iteration over a sequence of values.
def generator_name(arg):
# statements
yield something
String Handling in Python Questions
String handling questions assess your ability to manipulate and process text in Python. Proficiency in these areas is crucial for effective text manipulation and data parsing.
29) How do you concatenate strings in Python?
Strings can be concatenated using the ‘+’ operator, e.g.:
str1 = "Hello"
str2 = "World"
result = str1 + " " + str2
30) How do you reverse a string in Python?
In Python, strings can be reversed using slicing, e.g.:
reversed_string = "hello"[::-1]
print(reversed_string) #Output: "olleh"
31) What is the difference between str() and repr() in Python?
str() is used for creating readable string representations of objects, while repr() is used for creating unambiguous string representations that can be used to recreate the object.

32) How do you check for anagrams in Python?
Anagrams can be checked by sorting and comparing the strings, e.g.:
s1 = input("Enter the first word: ")
s2 = input("Enter the second word: ")
sort_s1 = sorted(s1)
sort_s2 = sorted(s2)
if len(s1) == len(s2) and sort_s1 == sort_s2:
print("Words are anagrams")
else:
print("Words are not anagrams")
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) Questions
OOP questions evaluate your understanding of concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation in Python. Mastery of OOP principles is essential for designing modular, reusable, and maintainable code.
33) What are the principles of OOP?
- Encapsulation: Bundling the data (attributes) and methods (functions) that operate on the data into a single unit, or class.
class Car:
def __init__(self, make, model):
self.make = make
self.model = model
def display(self):
print(f"Car: {self.make} {self.model}")
- Abstraction: Hiding the complex implementation details and showing only the essential features of the object..
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class Shape(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def area(self):
pass
- Inheritance: A mechanism where a new class inherits attributes and methods from an existing class.
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def speak(self):
raise NotImplementedError
class Dog(Animal):
def speak(self):
return "Woof!"
- Polymorphism: The ability to present the same interface for different data types.
class Bird:
def fly(self):
print("Flying")
class Airplane:
def fly(self):
print("Flying")
for obj in [Bird(), Airplane()]:
obj.fly()
34) What are the different types of Inheritance in Python?
- Single Inheritance: A class inherits from one superclass.
class Parent:
pass
class Child(Parent):
pass
- Multiple Inheritance: A class inherits from multiple superclasses.
class Base1:
pass
class Base2:
pass
class Derived(Base1, Base2):
pass
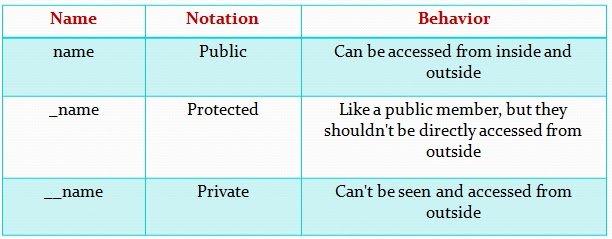
35) What are Access Modifiers in OOP?
- Public: Accessible from anywhere.
- Protected: Accessible within the class and its subclasses (prefix with a single underscore
_). - Private: Accessible only within the class (prefix with double underscores
__).
36) What is an Abstract Class?
An abstract class cannot be instantiated and often contains one or more abstract methods.
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class AbstractClassExample(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def do_something(self):
pass
37) What are Exceptions in OOP?
Exceptions are events that occur during the execution of programs that disrupt the normal flow of instructions.
38) What is the difference between Error and Exception?
Errors are serious issues arising mostly due to the environment in which an application is running, while exceptions are events that can be handled programmatically.
39) What is a constructor?
- Default Constructor: A constructor that takes no arguments.
class Example:
def __init__(self):
self.data = 42
- Parameterized Constructor: A constructor that takes arguments.
class Example:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
40) What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation is the bundling of data and methods that operate on the data within one unit, e.g., a class, restricting access to some of the object’s components.
41) What is the difference between Overloading and Overriding?
- Overloading: The ability to define multiple methods with the same name but different signatures.
- Overriding: A subclass provides a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass.
42) How can you call a parent function from a child function?
Using the super() function:
class Parent:
def display(self):
print("Parent method")
class Child(Parent):
def display(self):
super().display()
print("Child method")
31) What is the use of self keyword in a method?
The self keyword is used to represent an instance (object) of the class and allows access to the attributes and methods of the class.
44) What are Python decorators?
Decorators are functions that modify the functionality of another function, method, or class.
45) How do you use decorators to modify class methods?
The decorators are applied using the @decorator_name syntax above the function definition.
46) What are Python's special methods?
Special methods (also known as dunder methods) are predefined methods in Python classes that start and end with double underscores, e.g., __init__, __str__, __repr__, etc.
def decor(func):
def decorated_func():
print("I got decorated")
func()
return decorated_func
@decor
def ordinary():
print("I am ordinary")
ordinary()
# output : I got deocrated
# I am ordinary
Advanced Python Important Questions
Advanced Python questions delve into complex topics like memory management, metaclasses, decorators, and concurrency. These questions assess your deep understanding of Python’s inner workings and your ability to tackle sophisticated programming challenges.
47) What is the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) in Python?
The GIL is a mutex that protects access to Python objects, preventing multiple threads from executing Python bytecodes simultaneously, thus limiting the concurrency in Python multithreaded programs.
48) Explain Python's memory management.
Python uses automatic memory management through reference counting and garbage collection to manage the allocation and deallocation of memory.
49) How do you create a virtual environment in Python?
Virtual environments are created using venv or virtualenv, e.g.:
python -m venv myenv
50) What is metaclass in Python?
A metaclass is a class of a class that defines how a class behaves. A class is an instance of a metaclass.
51) What are Python's built-in modules?
Python built-in modules are pre-installed set of libraries that come with the Python installation.
Examples include sys, os, math, datetime, itertools, functools, etc.
52) What is the difference between __init__ and __new__ in Python?
__init__ initializes a newly created object, while __new__ is responsible for creating a new instance of the class.
53) What are the differences between @staticmethod and @classmethod?
@staticmethod defines a method that does not operate on an instance or class, while @classmethod takes a class as its first parameter and can operate on the class itself.
54) What is the None keyword in Python?
None is a special constant in Python representing the absence of a value or a null value.
55) How do you create an abstract class in Python?
Abstract classes are created using the ABC module from the abc library and must include at least one abstract method using the @abstractmethod decorator.
56) What are the different ways to create a copy of an object in Python?
Shallow copy using copy.copy() and deep copy using copy.deepcopy().
57) How do you perform static type checking in Python?
Static type checking can be performed using type hints and tools like mypy.
Functional Programming based Questions
The model that you construct in data science are based on algorithms, so knowledge of algorithm is core concept of data science. Algorithm-specific questions are mentioned below :
58) What are Python's built-in functions for functional programming?
Built-in functions include map(), filter(), reduce(), and lambda.
59) What is a lambda function in Python?
A lambda function is an anonymous function defined with the lambda keyword, e.g.:
add = lambda x, y: x + y
print(add(2, 3)) # 5
Miscellaneous Questions for Python Interview
Miscellaneous questions cover a wide range of Python topics that don’t fit neatly into other categories. These may include Python’s built-in functions, module usage, best practices, and various utility features essential for well-rounded Python proficiency.
60) What is the purpose of the __name__ variable in Python?
The __name__ variable determines if a module is being run directly or imported, e.g.:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Code block
61) How do you use the itertools module in Python?
The itertools module provides functions to create iterators for efficient looping, e.g.:
import itertools
counter = itertools.count(start=10, step=2)
print(next(counter)) # 10
print(next(counter)) # 12
62) How do you swap two variables in Python?
Variables can be swapped using tuple unpacking, e.g.:
a, b = b, a
63) What are Python's scope rules?
Python uses the LEGB (Local, Enclosing, Global, Built-in) rule for variable scope resolution.
64) How do you create a custom exception in Python?
Custom exceptions are created by subclassing the Exception class, e.g.:
class MyCustomException(Exception):
pass
65) What is a context manager in Python?
A context manager is a construct that allows the setup and cleanup of resources, typically used with the with statement.
Conclusion
Mastering the questions and concepts outlined in this guide is essential for excelling in Python interviews. By thoroughly preparing with these common interview questions and their answers, you’ll be well-equipped to showcase your expertise and confidence during the interview process.
If you’re looking to further enhance your Python skills and gain hands-on experience, consider joining Netmax Technologies. As a premier institution in IT training, we offer comprehensive courses ranging from 45 days to 4-6 months, designed to prepare you for real-world challenges and career success. Our experienced instructors and practical training approach ensure that you gain the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in the competitive field of Python development. Enroll today and take the first step towards becoming a proficient Python developer with Netmax Technologies!